6
- VM: the logical address space (ram + disk), Page: the amount of data that can swap between RAM and Disk at a given time, page table: maps “logical addresses” to physical/virtual memory, paging: swapping a page between ram and disk, page fault: data being accessed is not in RAM and needs to be swapped back, thrashing: when the OS spends more time paging than running apps
- every program has a PID and its own address space, types inc. system (core processes / started in boot) / user (apps/CLI) / daemon (background) / background tasks (scheduled / repetitive tasks eg backups) / interactive processes (continuous IO, eg vim) / zombie (completed execution but parent processes hasn’t read exit status)
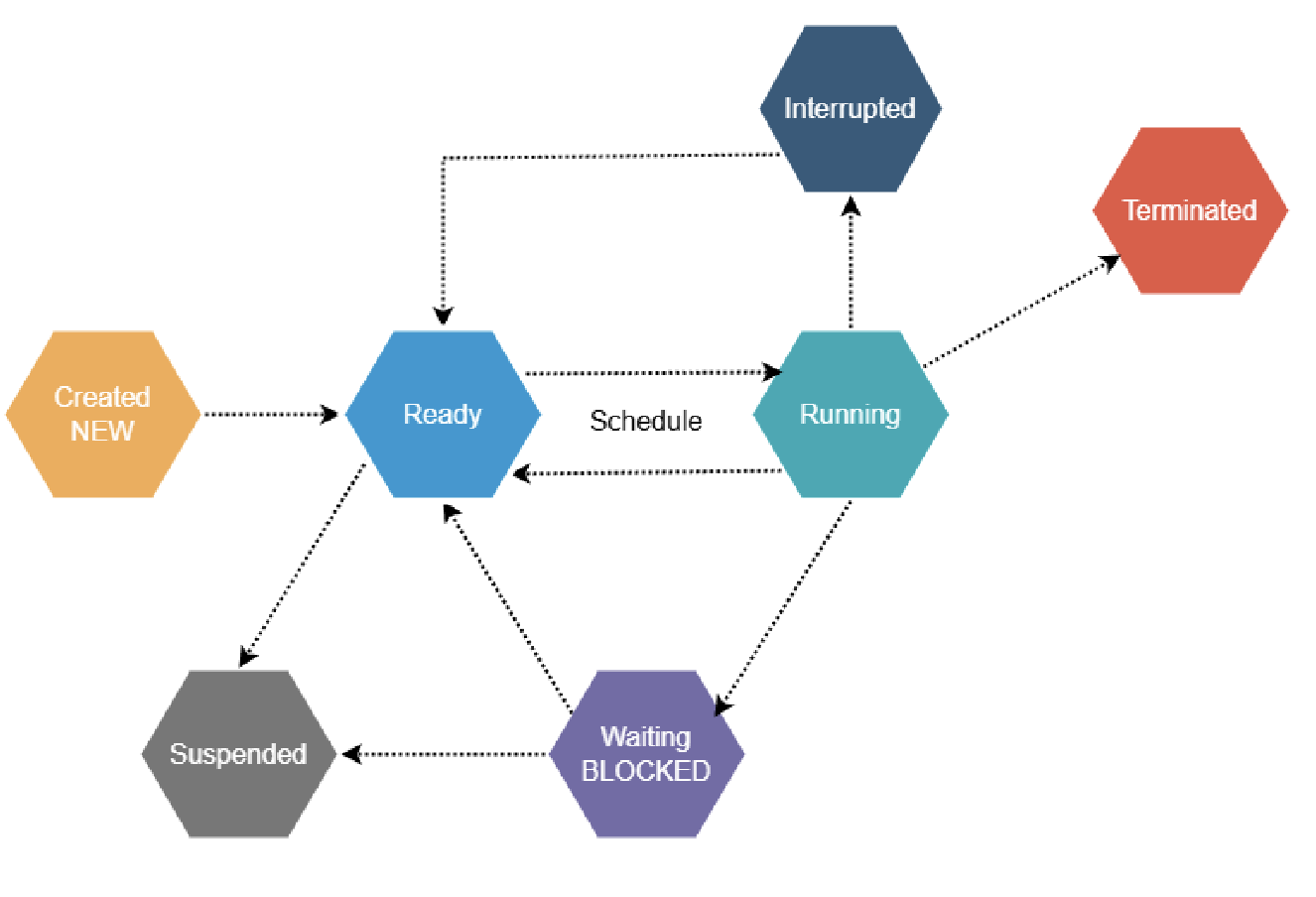
- new - process being created, ready - process has necessary resources and waiting for CPU time, running - on the cpu;one process per core can be in this state, waiting - paused waiting for i/o or resources, suspended - temp. halted and moved out of the ready queue, interrupted - pre-empted/interrupted, potentially moving back to the ready state when resumed, terminated - optional; process is moved out of main memory to secondary storage to free up memory; can be brought back
- IPC - Shared memory (2), file sharing, sockets (2), messages (posix MQ) (2), pipes (2), locks, semaphones, signals
- kernel resource management - cpu scheduling (algorithms include round robin, priority), memory/file/io/networking management
- deadlock prevention - resource ordering, lock timeout, avoid mutual locking
8
- computer architecture - memory address register (MAR), memory data register (MDR), accumulator (AC), program counter (PC), current instruction register (CIR)
- bus - pathways for data transfer between cpu/memory/peripherals, ie keyboard/mouse/scanner/leap motion; data bus, address bus, control bus
- fetch decode read write-back execute
- representation - 1/0, transmission - circuits/buses between components (cpu/ram), interpretation - pulses of voltage (high 1 low 0), synchronization - clock pulses
10
- topologies - bus, star, mesh
- osi - physical>data link>network>transport>session>presentation>application
- protocols - tcp/ip, smtp/pop/imap, ftp/s, rdp/ssh, http/s, udp, icmp, dns, dhcp
- segmenting - basically subnetting, osi L3 (IP), broadcast/loopback/unknown,
Mail transfer agent MTA vs mail user agent MUA
User agent: Email clients Transfer agent: SMTP / POP3 servers
Binary
ASCII: a/97, A/65, z/122, Z/90